Designing Flexible Technologies for the Cities We Actually Need

Introduction: The Convergence of Urban Intelligence and Robotic Flexibility
Smart cities are not a futuristic concept anymore. They are being built, one data layer, one automation module, and one policy reform at a time. From Toronto to Singapore, municipalities are embracing technologies that support sustainable, efficient, and equitable living. Central to this evolution is the ESG framework, Environmental, Social, and Governance goals, which now guide not only investor priorities but also urban planning strategies.
In this context, soft robotics emerges as a uniquely well-positioned enabler. Unlike traditional industrial robots, soft robotic systems can operate in dynamic, human-centered environments without the risks of rigidity and forceful interactions. Their gentle, adaptive nature makes them ideal for use cases where safety, energy-efficiency, and inclusivity intersect. But how exactly do soft robotic solutions align with ESG benchmarks in smart cities?
Integrating Soft Robotics into Urban Supply Chains
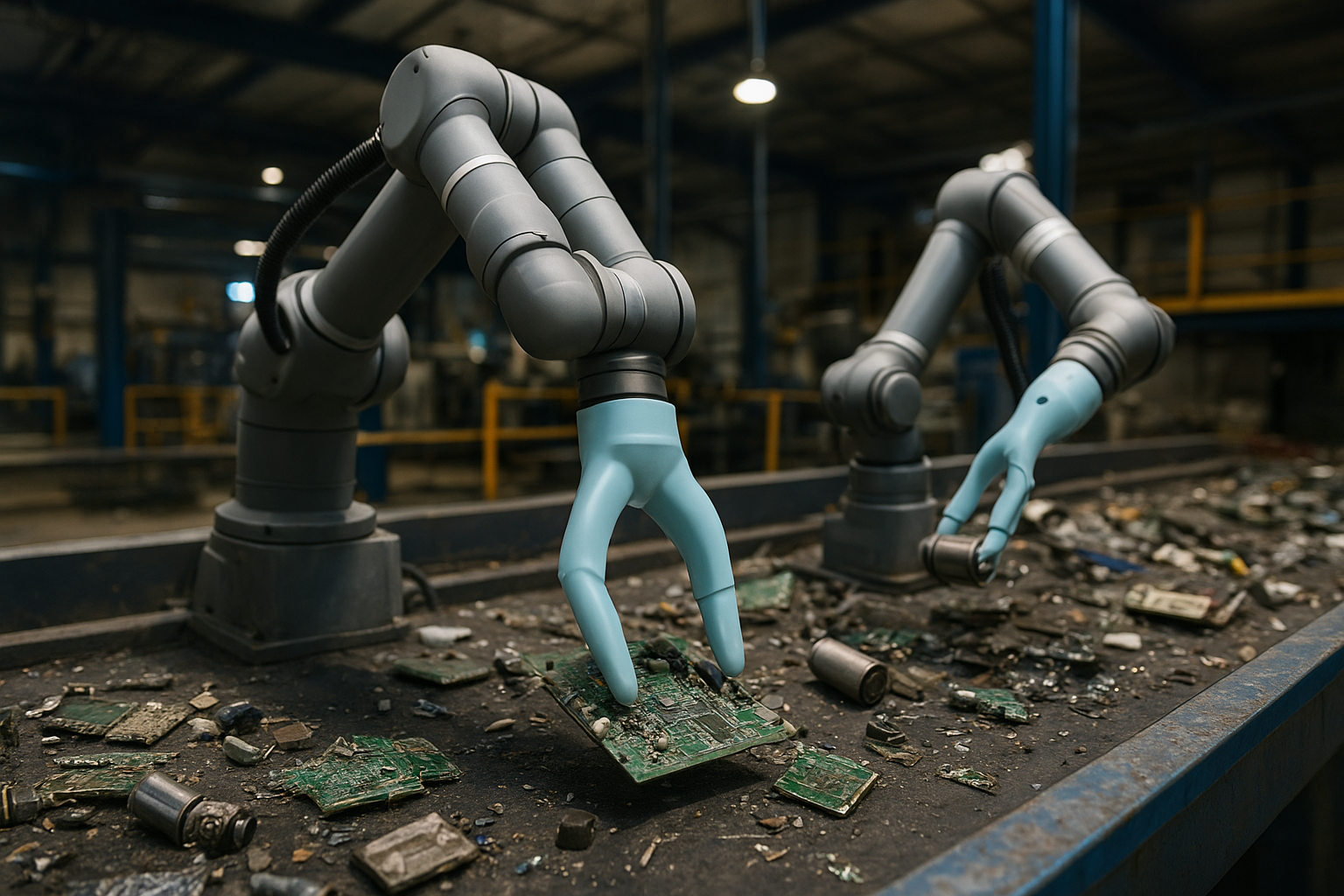
As urban populations surge, so does the demand for smarter, cleaner, and more resilient supply chain infrastructures. Traditional logistics systems, centralized, energy-intensive, and rigid, are struggling to keep up with the pace and complexity of city life. This is especially evident in last-mile delivery, micro-fulfillment, and food distribution.
Soft robotics can help reimagine this landscape. By equipping automated urban warehouses with soft robotic arms and grippers, cities can decentralize logistics, embedding micro-distribution hubs directly within residential or mixed-use smart buildings. These soft robotic systems excel at handling delicate, deformable, or irregular-shaped items, such as meal kits, pharmaceuticals, or locally harvested produce, without damage or reconfiguration downtime.
When paired with AI-based vision and control, these robots not only optimize throughput but also reduce the need for excessive packaging materials, lowering plastic waste and supporting circular economy principles.
Moreover, the low power requirements of pneumatic soft actuators, especially when compared to traditional electromechanical solutions, contribute directly to a city’s energy consumption reduction targets, reinforcing progress under the Environmental pillar of ESG.
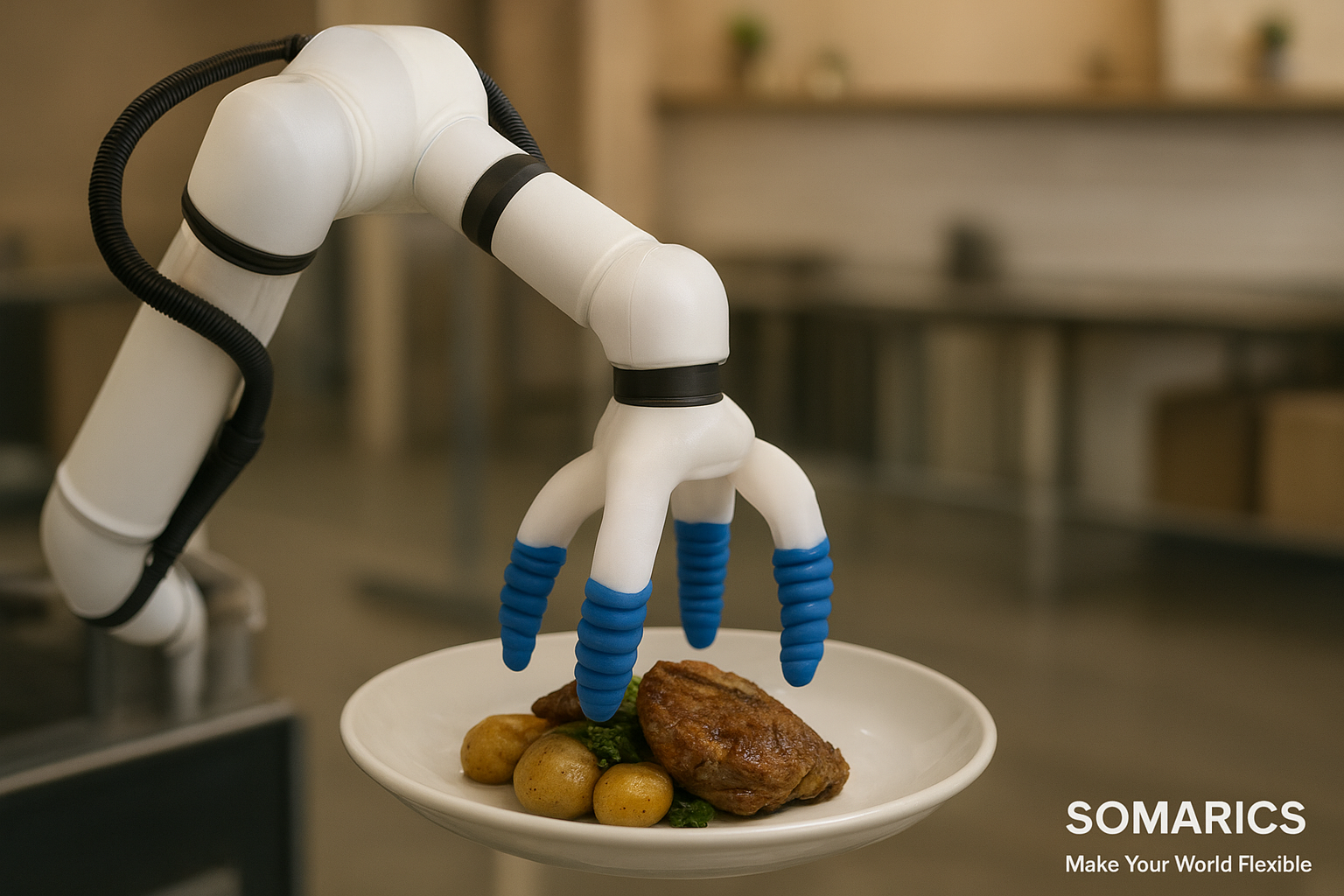
Enhancing Safety and Inclusion in Public Services
ESG-compliant cities are inclusive by design. Urban environments must support a wide spectrum of physical and cognitive abilities, particularly as populations age and disability rates rise. Yet, many city services and infrastructures remain inaccessible, either due to physical constraints or lack of adaptability.
This is where soft robotics’ human-centric design philosophy becomes critical. Unlike rigid automation systems, soft robots can physically interact with people, children, seniors, or persons with limited mobility, without risk of injury. They can be embedded into public kiosks, elevators, transit stations, or autonomous service robots, offering touch-based support, gesture-triggered interactions, or gentle object handling.
For example, in smart eldercare centers, soft robotic arms can assist with meal preparation, dressing aids, or medication dispensing, tasks that require delicacy, empathy, and fail-safe response. These are not just engineering achievements, but ESG milestones under the Social dimension, empowering vulnerable populations through dignified technology.
In schools or libraries, soft robotic assistants can support children with special needs by engaging them in interactive learning or physical play, without overwhelming them with aggressive movements or noise.
Enabling Ethical Data Collection and Responsible AI
Smart cities thrive on data, but not at the expense of privacy. Public backlash against intrusive surveillance technologies has made responsible AI and data governance essential to ESG credibility. Soft robotic systems, especially those designed for physical tasks rather than surveillance, offer an alternative path.
By embedding tactile, force, and environmental sensors into soft robotic elements, cities can gather actionable insights into real-world interactions, such as how often public infrastructure is used, where cleaning is needed, or how waste disposal behaviors are changing, without capturing any personal identifiers.
This allows urban managers to optimize city services, perform predictive maintenance, and allocate budgets intelligently, all while respecting citizen autonomy. In ESG terms, this strengthens the Governance pillar, aligning with evolving ethical standards and regulatory expectations on data use.
Adaptive Infrastructure and Emergency Response
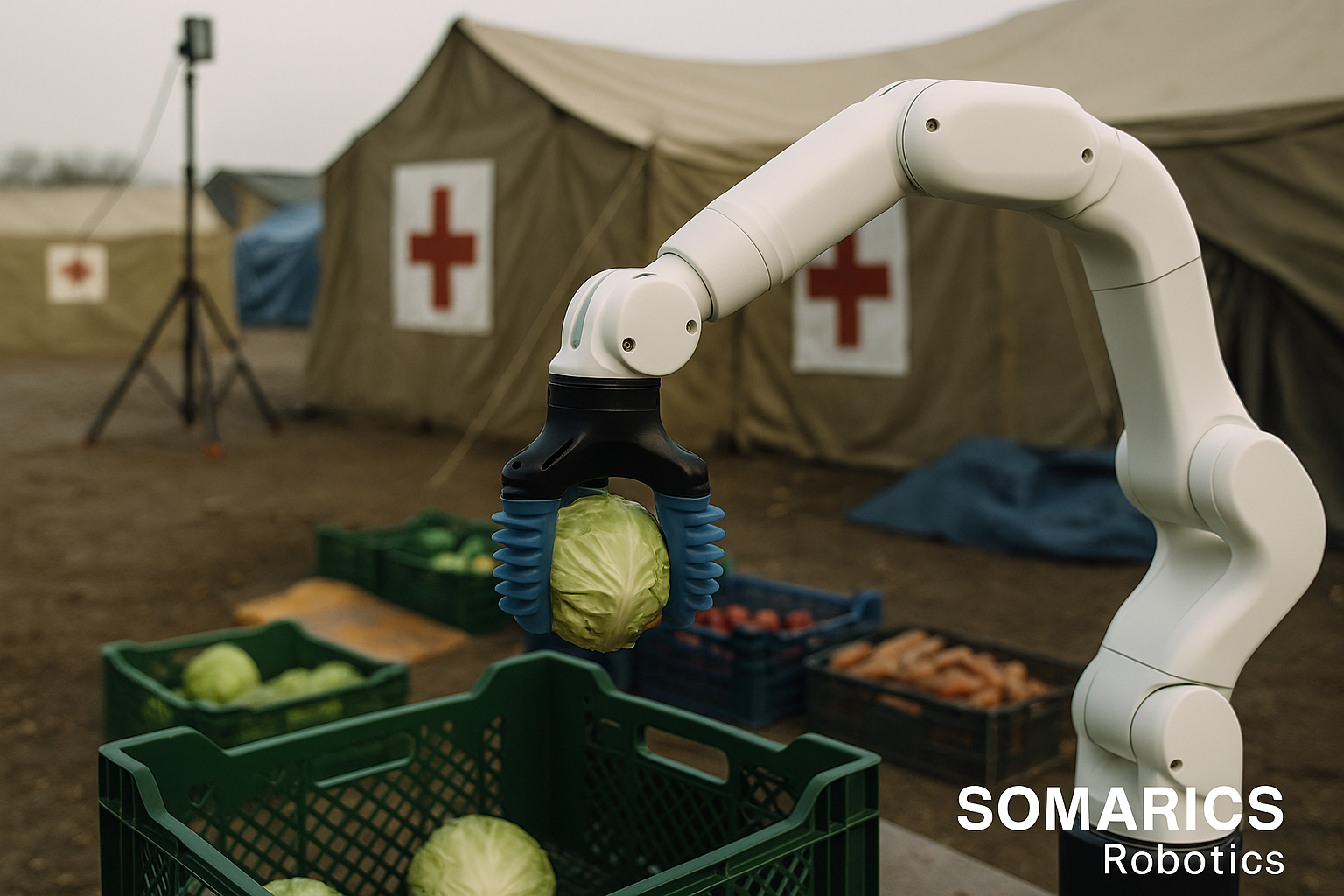
As climate instability, health crises, and social unrest become more frequent, urban resilience is no longer a choice; it’s a design requirement. The cities of the future must reconfigure on demand, creating and dissolving functions as needed, often with minimal time and resources.
Soft robotics introduces a new kind of infrastructure fluidity. Portable, reprogrammable, and modular by design, soft robotic platforms can be rapidly deployed in pop-up clinics, disaster relief hubs, or emergency logistics centers.
Consider a scenario in which a city faces a heatwave-induced blackout. Mobile cooling stations equipped with soft robotic systems could assist with distributing water, checking basic health parameters, or guiding vulnerable residents. In a pandemic, soft robots can handle sterilization, contactless medicine transfer, or even human interaction tasks, reducing risks for frontline workers.
From a risk mitigation and continuity perspective, this elevates ESG preparedness scores and demonstrates institutional adaptability, making the city more attractive to impact investors and citizens alike.
Soft Robotics in Urban Agriculture and Food Security
Urban food systems are under intense pressure, driven by land constraints, supply chain volatility, and climate shocks. Smart cities are responding with indoor farms, rooftop greenhouses, and automated hydroponic facilities, all of which can benefit from soft robotic integration.
Soft robotic grippers are particularly well-suited to harvest delicate crops, manage planting systems, and handle packaging, all within confined, humidity-sensitive environments. Their gentle contact reduces bruising and waste, while their ability to conform to variable shapes makes them ideal for mixed-crop setups, a growing trend in vertical farming.
The synergy here is clear: soft robotics helps cities build resilient, hyperlocal food systems with minimal labor overhead and maximum sustainability impact. This contributes to both Environmental and Social ESG indicators, while also creating a potential platform for public-private co-investment in agri-tech innovation zones.

Unlocking ESG-Aligned Investment and Policy Support
Municipalities, public-private partnerships, and impact investors are increasingly aligning funds with ESG metrics. Technologies that score highly on carbon reduction, safety, and inclusivity attract easier access to:
- Green infrastructure bonds
- Smart city innovation grants
- Inclusive tech procurement programs
- ESG-focused venture funds and accelerators
By integrating soft robotics into their pilot projects, startups like SOMARICS can establish early partnerships with urban innovation offices, infrastructure developers, or civic technology integrators, thereby securing both financial and strategic capital.
This isn’t just an engineering opportunity, it’s a market positioning strategy. And in a competitive ESG-conscious ecosystem, timing and alignment matter as much as technical capability.
Conclusion: A Strategic Role for Soft Robotics in the Smart Cities of Tomorrow
In the rapidly maturing landscape of smart cities, technology is not enough. Cities are seeking empathetic automation, systems that serve people, adapt quickly, and do so without harming the planet. Soft robotics delivers precisely this: not just functionality, but flexibility, safety, and civic compatibility.
From food security to public infrastructure, and from eldercare to ethical data collection, soft robotic systems offer more than novelty; they offer infrastructure trustworthiness, a quality increasingly prioritized by governments and ESG-driven stakeholders alike.
For companies like SOMARICS, this is a moment of alignment, a rare confluence of market demand, societal need, and technological readiness. Smart cities are not waiting. The time to engage, pilot, and lead is now.
SOMARICS – Make Your World Flexible!
Let’s Do It!