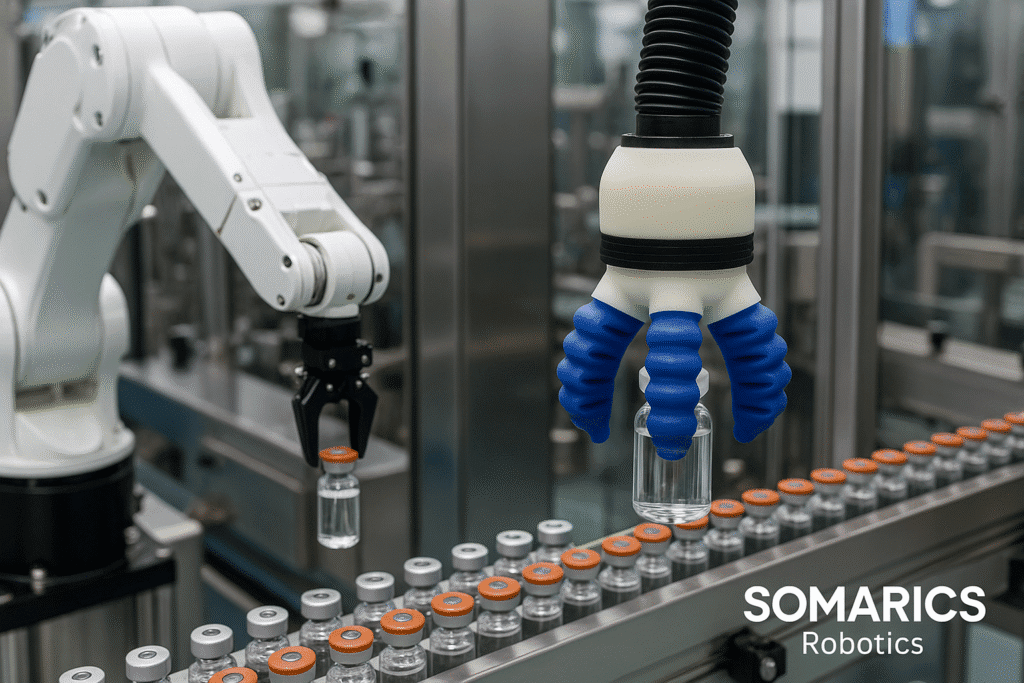
In the rapidly evolving world of pharmaceuticals, the demand for precision, sterility, and adaptability is more pressing than ever. As drug development becomes increasingly complex and manufacturing systems require greater flexibility, traditional robotics often struggles to meet modern production needs. This is where soft robotics steps in, offering a revolutionary approach to automation that redefines how pharmaceutical companies handle delicate materials, ensure cleanroom compliance, and enable human-robot collaboration.
A Changing Landscape in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical manufacturing has long relied on rigid, pre-programmed systems that excel in performing repetitive, high-throughput tasks. However, the industry’s shift toward personalized medicine, smaller batch sizes, and stringent sterility requirements is exposing the limitations of these conventional systems.
Production lines now require modular, flexible, and easily reconfigurable systems to support product variations, respond quickly to changing regulations, and reduce human error. Soft robotics offers exactly this, combining compliance with adaptability to address a wide range of challenges in pharmaceutical environments.
What Are Soft Robots, and Why Do They Matter Here?
Soft robots are machines constructed from flexible materials such as silicone, rubber, and elastomers, often powered by pneumatic or hydraulic actuators. Their inherent deformability enables them to conform to objects of varying shapes, absorb impact without damage, and interact with fragile items without exerting excessive force.
In pharmaceutical settings, this means that soft robotic grippers or manipulators can handle delicate vials, ampoules, blister packs, and syringes without breakage or contamination. Their gentle touch is particularly valuable in secondary packaging and assembly lines where fragile or sterile components must be transferred, filled, or labeled with minimal disruption.
Sterility and Cleanroom Compatibility
Sterility is non-negotiable in the pharmaceutical industry. Any contamination can result in lost batches, regulatory violations, and potentially dangerous outcomes for patients.
Soft robotics brings a clear advantage in sterile environments. Many soft actuators and grippers can be manufactured using FDA-approved, autoclavable, and chemically resistant materials, making them suitable for direct integration into cleanrooms. Moreover, the simplicity of their structure, fewer moving parts and no exposed lubricants, reduces the risk of particle generation.
These features make soft robots ideal for use in:
- Aseptic packaging
- Sterile fill-finish operations
- High-speed sorting and transfer of containers
- Inspection tasks within laminar flow hoods

Human-Robot Collaboration in Sensitive Environments
One of the major advancements driving automation is the rise of collaborative robots, or cobots, designed to work safely alongside human operators. Soft robots naturally lend themselves to this role.
Unlike rigid robots that require protective cages and careful safety programming, soft robots operate with compliant surfaces and limited force output. This significantly reduces the risk of injury and allows technicians to interact directly with robotic systems, even in small spaces.
In tasks such as line clearance, material handling, or co-inspection, soft robots can support human workers in repetitive or ergonomically challenging actions. This collaborative framework enhances workplace safety, reduces musculoskeletal injuries, and frees up human talent for value-added tasks.
Reducing Product Waste and Increasing Yield
In pharmaceutical processing, waste is costly, not only in financial terms but also in regulatory compliance and production timelines. Damaged components, mislabeling, and breakage during handling all contribute to yield losses.
Soft robotic systems mitigate these risks by applying controlled and uniform force. For example, when handling fragile glass containers, a soft gripper can dynamically adjust pressure to avoid slippage or crushing. Similarly, during secondary packaging, soft end-effectors can gently nest products into trays or boxes without scuffing or shifting.
This level of control improves handling quality and directly translates to higher yields, fewer rejects, and more reliable processes.
Enhancing Adaptability in Modular Production Lines
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting modular manufacturing systems to respond quickly to changing market demands and regulatory updates. Soft robotics fits perfectly into this framework.
A single soft gripper can be used to handle different container shapes and sizes without requiring hardware changes, reducing downtime and increasing operational flexibility. Reprogramming a soft robot to adapt to a new product batch often requires minimal intervention, enabling faster changeovers and lower overhead costs.
Furthermore, integrating sensors within soft robotic structures (e.g., pressure, temperature, or proximity sensors) enables real-time feedback that supports adaptive control strategies. These smart systems can monitor conditions and respond dynamically to ensure consistent quality across diverse processes.
Applications Across the Pharmaceutical Supply Chain
Soft robotics can play transformative roles across various stages of the pharmaceutical value chain:
1- Research and Development (R&D)
- Gentle handling of lab samples, pipettes, or biological tissues
- Automated liquid dispensing using soft-actuated precision systems
2- Manufacturing
- Transfer of sterile vials and containers between processing units
- Secondary packaging (labeling, boxing, tray nesting)
- Handling blister packs and fragile capsule forms
3- Quality Control and Inspection
- Manipulating and presenting delicate items to vision systems
- In-line defect detection support through soft, repeatable positioning
4- Distribution and Fulfillment
- Customized packing for temperature-sensitive or fragile goods
- Collaborative packaging with human operators in logistics centers
Addressing Regulatory and Validation Challenges
Pharmaceutical automation must comply with stringent validation protocols, including Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), FDA 21 CFR Part 11, and ISO 14644 cleanroom classifications. Integrating soft robotics into such environments requires careful system design and documentation.
Fortunately, many soft robotics platforms are now being designed with GMP compliance in mind, including full traceability, validated cleaning protocols, and integration with electronic batch records (EBRs). As validation frameworks evolve, the inclusion of soft robotics in FDA or EMA-compliant facilities is becoming increasingly feasible and scalable.
The Role of AI and Data in Future Applications
The next generation of soft robots will not only be flexible in structure but also in decision-making. By incorporating AI algorithms and machine learning models, soft robots will be able to recognize objects, optimize grip strategies, and even predict failure modes.
In pharmaceutical settings, this intelligence could enable predictive maintenance, adaptive product sorting, and autonomous changeovers, all of which contribute to leaner and more agile production systems. Data gathered through sensors in soft robots can feed into centralized analytics platforms to monitor trends, detect anomalies, and drive continuous improvement.
Strategic Advantages for Pharmaceutical Innovators
For companies looking to lead in pharmaceutical innovation, soft robotics offers a strategic edge:
- Speed to market through faster, modular production
- Improved product safety with lower risk of contamination
- Greater ROI via yield improvement and operational agility
- Workforce sustainability through ergonomic automation
With increasing pressure on pharmaceutical companies to innovate faster and deliver safer products at lower costs, soft robotics stands out as a foundational technology for the future of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
So again: The Future Is Soft, and It’s Already Here
Soft robotics is no longer a futuristic concept; it is becoming a present-day solution for some of the most critical challenges in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Its unique blend of flexibility, safety, cleanliness, and adaptability positions it as an essential component of modern pharmaceutical operations.
As the industry continues to adopt more intelligent, human-centered, and sustainable technologies, the role of soft robotics will only expand. Whether it’s handling fragile vials, assisting technicians in sterile rooms, or enabling faster production cycles, soft robots are enabling pharmaceutical companies to build smarter, safer, and more resilient systems.
At SOMARICS Robotics, we are committed to enabling this transition. By developing advanced soft robotic solutions tailored for real-world pharmaceutical challenges, we empower companies to stay ahead in a rapidly changing landscape.
To explore how SOMARICS can help your pharmaceutical facility evolve, visit our Products page or contact our team of experts.